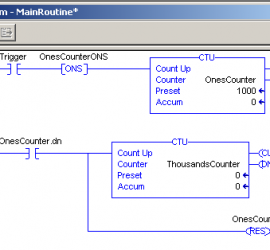
Proportional Settings for ControlLogix PID Enhanced (PIDE)
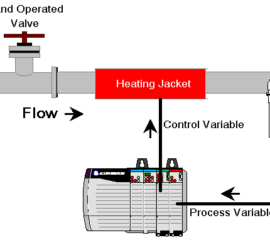
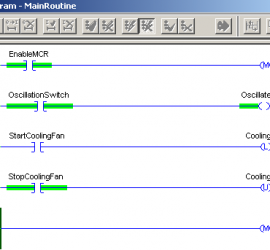
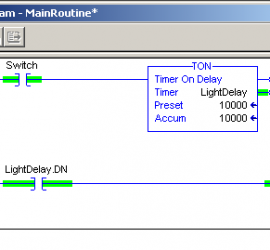
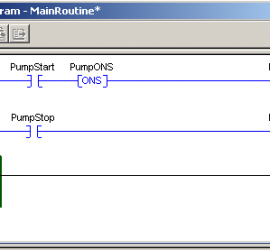
Introduction for Proportional Settings for ControlLogix PID Enhanced (PIDE) In this section, we’ll discuss the proportional settings for Controllogix PID Enhanced (PIDE). It’s important to remember the difference between the PID in ladder logic vs. the function block PIDE. The main difference is that the ladder logic PID instruction is Read More »