Kenbak-1 Multiplication
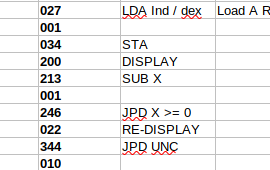
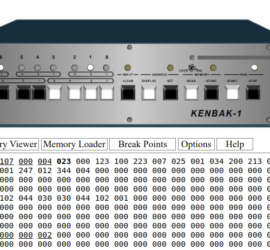
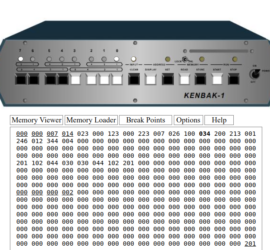
Introduction to Kenbak-1 Multiplication Kenbak-1 Multiplication involves creating loops. Being designed in 1971, the Kenbak-1 has a limited instruction set. That limited instruction set presents some good challenges. These challenges force us not only to understand the Kenbak-1 itself, but also understand more about mathematics. There is no direct instruction Read More »